Generations
Computer Hardware
and Software have come a long way since digital computing was
first conceived. As each major technological breakthrough heralded a
new hardware generation, software too progressed in sophistication:
| Gen |
Hardware |
Software |
| 1 |
Mechanical
Computers
Physical
switching technology (eg. "steam driven" calculating
machines)
|
Binary
Instructions
respresented as a sequence of 1's and 0's. Very low level,
verbose but executed directly on transistors
|
| 2 |
Vacuum
Tube- Based Computers
Vacuum tubes (specialised 'bulbs') perform the same job switches
did in mechanical computers (2 states = ON/OFF). Huge, hot
and fragile, took time to 'warm up'.
|
2GL-ASM
Mnemonic
Binary= Assembler Language. Clusters of binary instruction
codes given a name (eg. MOV, POP, AND). Low level, verbose,
executed via 'instruction sets' burnt on to IC's.
|
| 3 |
Transistor-Based
Computers
Each
'tiny' transistor did the same job as a valve (ie. provided
an on/off switch). Invention heralded the 'solid state' revolution
in consumer radios and other electronic goods.
|
3GLs
Procedural
Languages - say what you want to happen and provide instructions
for how you want it to be done as well (eg. Pascal, BASIC,
COBOL, FORTRAN, C). Clusters of ASM codes grouped under named
instructions (eg. PRINT, READ). Relatively high level english-like
instructions, interpreted into ASM before executed.
|
| 4 |
Integrated
Circuit-Based Computers
Many
microscopic transistors etched onto a single silicon chip
- miniaturisation with the 'computer on a chip'.
|
4GLs
Declaritive
Languages - say what you want to happen, not how (eg. SQL,
PROLOG, LISP). High level, compact english-like commands
|
| 5 |
Massive
Parallel Processing
Multiple
processors sharing the tasks, huge bandwidth (in it's infancy
currently)
|
5GLs
Natural
Language with ability to convert near normal (or formalised)
communication into commands - understanding context and intention.
Not available yet.
|
Database
Components
There are typically
3 components to a traditional '70s style Info Sys.
- Database
= the set of stored facts or propositions
- DBMS =
DataBase Management System, that operates on the database and provides
the means for retrievals, updates etc.
- Application
Programs = providing a human-computer interface, ('friendly front-end'),
generally menu or command driven, provide a 'relatively' easy means
of communication with the DBMS which then operates on the DB
Allied Concepts:
- data representation
- the 'physical' representation of the data (on the disk, say)
- independence
- whether the system could be run on different hardware
- redundancy
- the storage of a particular fact in more than one place, or the
storage of a fact that is an amalgam of other facts - leads to update
anomalies and possibly inefficient data representation.
- query capability
- an 'english' like language for 'ad-hoc' enquires and requests
- performance
- response time - application specific
- optimization
- ensuring the operational performance is as fast and as direct as
possible
- cost effectiveness
- including design, implementation, population and maintenance (possibly
on-going)
- security
- protection against unauthorised access
- integrity
- 'correctness' and consistency of stored facts
Fifth Generation
Information Systems (5GIS)
It has been proposed
that an Information System based on a 5th Generation Language could
differ from it's predecessors radically.
There would be two
main transaction types when using a 5GIS:
- Specification
of the Universe Of Discourse (UoD). The UoD of an information
system is the entire description, of all facts and relationships that
exist in the situation being modelled by the IS
- Querying
the system about the UoD
Although true
5GIS's don't yet exist, much work has been done towards that goal,
with early DB research still aiming at the relational ideal.
When building an
'old style' database, most effort is expended in the implementation
stages (the building of the storage containers, interface and controlling
the DB management system and client programs).
When building a
5GIS, most of the work is done in the design stage, where a complete
formal description of the UoD is complete with facts (both type and
context), rules governing these facts and constraints. Implicit in the
specification of the UoD are all of the constraints and derivations
that would have been handled by client programs in an old style database.
Turings Test Of
Intelligence
It
is suggested that one of the important building blocks for a true
5GIS is an interface that displays intelligence - but how do we guage
intelligence?
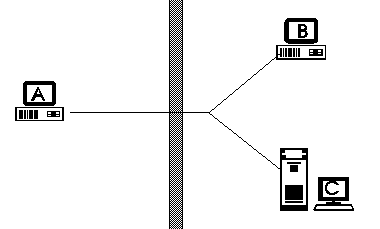
Alan Turing proposed
a test involving humans conversing with other humans and computers.
In this test, Human A 'converses' via 'chat' software with person B
(male pretending to be female) on the otherside of an opaque wall (via
a computer terminal) in natural language about a desired topic. Human
B eventually hands over the conversation to Machine C.
IF A can tell the difference between B and C
then the machine IS NOT intelligent
else the machine IS intelligent
To date, NO computer
has passed this test... however, on restricted topics and using some
formalisation of the 'natural language' used in the conversation, some
computers have performed at a 'human' level or better.
eg. Chess computers,
Blood disorder diagnosis (so-called 'Expert systems' where the UoD
is specified and NARROW)
Universe Of Discourse
human <------------> human
(natural language communication)
human <------------> 5GIS
Using FNL (Formalised
Natural Language - which has specific conventions, syntax and allowances
for cultural differences in expression), communication with a 5GIS should
be similar to communicating with a human educated in that field.


